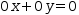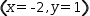5.7 Redundant Equations
The system
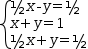
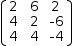 |
 |
| (a) Matrix | (b)Reduced form |
The last row in Figure
5.2
(b) means
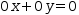
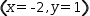
The system
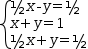
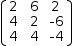 |
 |
| (a) Matrix | (b)Reduced form |
The last row in Figure
5.2
(b) means